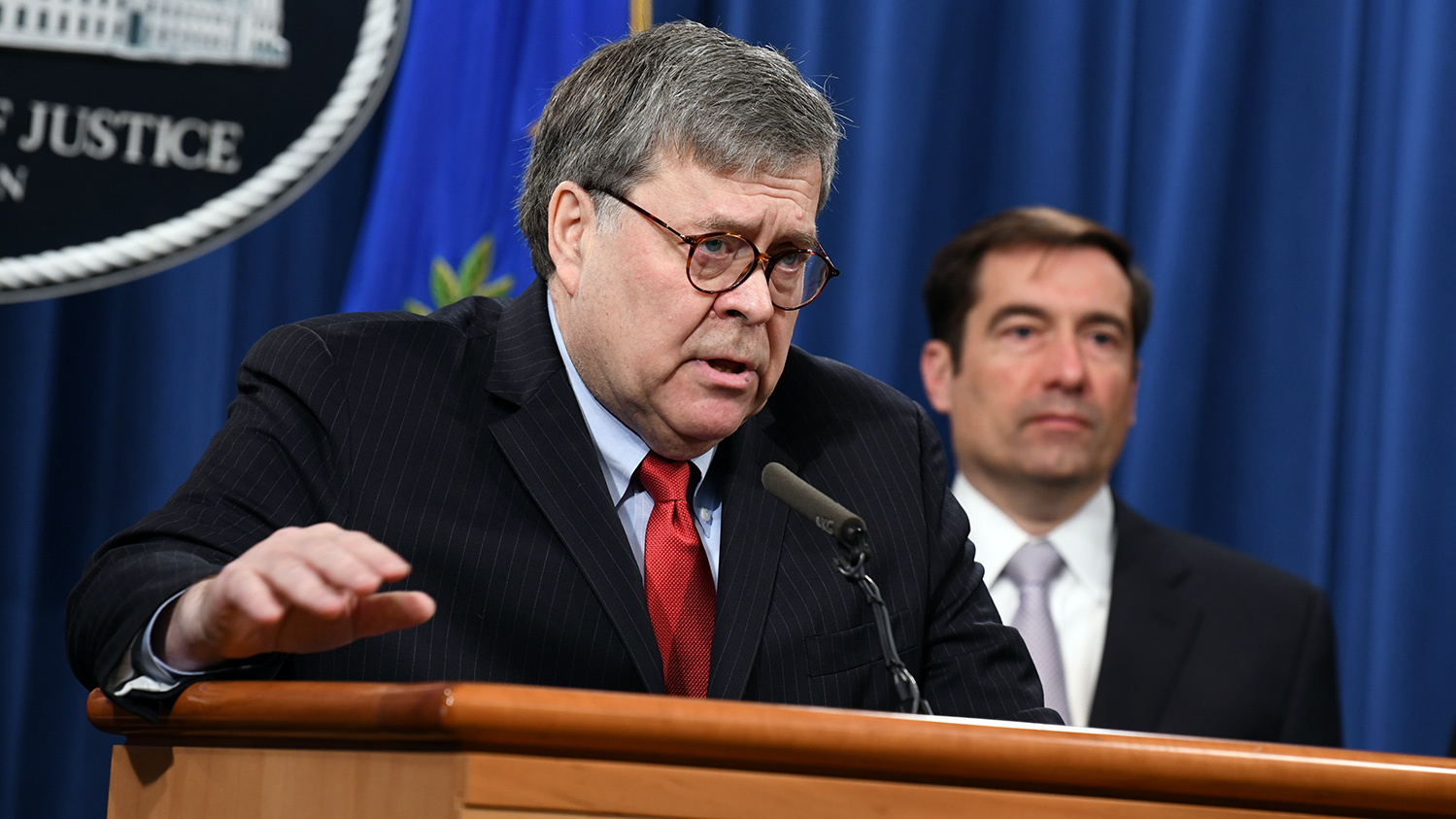
Today the US Department of Justice (DOJ) publishes four reform proposals to Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act that would encourage online platforms to promote free speech while addressing illicit content with greater transparency.
US Attorney General William Barr issued a statement today saying that Section 230 of the Communications Decency Act of 1996 was outdated and needed to be reformed to face the challenges surrounding today’s online content.
The four reform proposals include:
- Promoting Open Discourse and Greater Transparency
- Incentivizing Online Platforms to Address Illicit Content
- Clarifying Federal Government Enforcement Capabilities to Address Unlawful Content
- Promoting Competition
“Taken together, these reforms will ensure that Section 230 immunity incentivizes online platforms to be responsible actors,” said AG Barr.
“These reforms are targeted at platforms to make certain they are appropriately addressing illegal and exploitive content while continuing to preserve a vibrant, open, and competitive internet,” he added.
Barr’s remarks come one day after Google became embroiled in yet another scandal, in which the tech giant was accused of threatening to demonetize media outlets Zero Hedge and The Federalist, allegedly at the behest of NBC, for not taking steps to remove inappropriate comments submitted by outside parties.
Sen. @TedCruz: “Google today has become like the Empire in Star Wars. What they’re doing with this step is testing the Death Star.” pic.twitter.com/i4EaaTTIiV
— Benny (@bennyjohnson) June 17, 2020
According to the Washington Times, “In explaining its decision, Google said it found comments made on Federalist articles to be dangerous or offensive, and demanded the comment section be removed.”
Our policies do not allow ads to run against dangerous or derogatory content, which includes comments on sites, and we offer guidance and best practices to publishers on how to comply. https://t.co/zPO669Yd0p
— Google Communications (@Google_Comms) June 16, 2020
One of the new reform proposals from the DOJ will look to promote free and open discourse online and encourage greater transparency between platforms and users.
“The Department proposes adding a statutory definition of ‘good faith,’ which would limit immunity for content moderation decisions to those done in accordance with plain and particular terms of service and accompanied by a reasonable explanation” — DOJ reform reccomendation
Recommendations for this particular reform were all centered around content moderation — the very subject of yesterday’s kerfuffle between Google and the news outlets.
The DOJ’s content moderation reform recommendations include:
- Replacing Vague Terminology
- This reform would focus the broad blanket immunity for content moderation decisions on the core objective of Section 230—to reduce online content harmful to children—while limiting a platform’s ability to remove content arbitrarily or in ways inconsistent with its terms or service simply by deeming it “objectionable.”
- Providing Definition of Good Faith
- The Department proposes adding a statutory definition of “good faith,” which would limit immunity for content moderation decisions to those done in accordance with plain and particular terms of service and accompanied by a reasonable explanation, unless such notice would impede law enforcement or risk imminent harm to others.
- Explicitly Overruling Stratton Oakmont to Avoid Moderator’s Dilemma
- The Department proposes clarifying that a platform’s removal of content pursuant to Section 230(c)(2) or consistent with its terms of service does not, on its own, render the platform a publisher or speaker for all other content on its service.
You can check out the details for all four reform recommendations here.
Tech products, culture are ‘designed intentionally for mass deception’: Ex-google ethicist testifies https://t.co/ewkeWBBvxF via @thesociable
— Joe Rogan (@joerogan) January 17, 2020
AG Barr said that online platforms should be both free to innovate and responsible for moderating content.
“These twin objectives of giving online platforms the freedom to grow and innovate while encouraging them to moderate content responsibly were the core objectives of Section 230 at the outset,” said Barr.
According to the DOJ, “Section 230 was originally enacted to protect developing technology by providing that online platforms were not liable for the third-party content on their services or for their removal of such content in certain circumstances.
“This immunity was meant to nurture emerging internet businesses and to overrule a judicial precedent that rendered online platforms liable for all third-party content on their services if they restricted some harmful content.”
It’s been some 25 years since Section 230 was written, and the DOJ believes it’s “ripe for reform.”